D104 Low Impedance Conversion
D104 conversions on the web seem to be exceptionally prone to error, or to
poor design. Some
pages have FET’s drawn backwards, some pages have needless RF chokes and
parts, and some pages have incorrect biasing methods. Many systems have no
bypassing of power supply sources.
RF chokes are commonly used to decouple leads, but we have to be careful when
using them. A series RF choke and shunt bypass capacitor actually behaves like a
network. Above a certain frequency, it can indeed reduce voltage passing though.
On lower frequencies, it can increase voltage passing through! If possible, we
should really use a suppression ferrite (appearing resistive rather than
inductive) or a resistor in RF filters. This prevents the circuit from having
resonances, and prevents accidentally stepping up RF voltage and increasing RF feedthrough on some
frequencies. Because current flows through a bypass or decoupling system,
it isn’t always possible or practical to use a RF filter resistance. In such cases
suppression beads over a suitable conductor, or an inductor shunting the resistor,
can limit unwanted RF peaks through the RF bypass/filter system while still
passing dc or low frequency audio currents with minimal voltage drop.
Here is a very simple circuit that works!
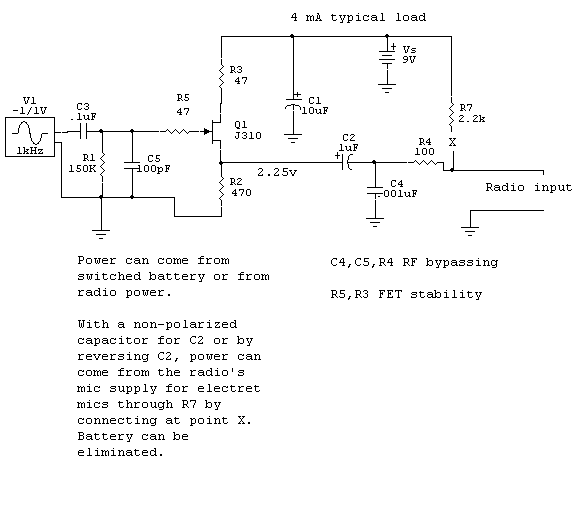
R1 affects frequency response. Higher values increase bass response. It will
also affect gain to some extent, depending on how the element output varies into
different load impedances. R1 should primarily be selected to control element
frequency response.
R4 is RF decoupling
C2 or C3 can be reduced in value to roll-off low frequency response
Keep leads on C4 and C5 short, and keep R4 and C4 near the audio cable output
where the shield is grounded
C5 can be increased in value to roll-off highs
V1 is the mic element
Note: use either R7 or a battery. Switch the battery off when not using the
microphone
If the mic audio pin supplies voltage, R7 can connect to the mic audio pin.
If a different pin supplies mic voltage, connect R7 to that pin.
|
